Program Overview :
Mission:
The program aims to equip students from diverse academic backgrounds with the English language skills in its main fields (linguistics, literature, and translation) required for the labor market.
Objectives:
- Provide students with a solid foundation in English, which includes, linguistics, literature, and translation.
- Develop graduates effective oral and written communication skills in line with their academic disciplines.
- Prepare students for various professional sectors by fostering responsibility and adaptability to the evolving demands for local and global labor markets.
Admission Requirements:
- The student's accumulative GPA.
- The extent to which students' individual study plans align in course distribution for the minor or dual program, so that the department is not required, as far as possible, to create exceptional class sections for them .
- When applying for a minor or dual program, the student must submit an individual registration plan issued by their department or academic advisor in the primary major, in accordance with Paragraph Three of Rule Six and Rule Ten of the governing regulations.
Awarded Qualification:
Upon completion of 39 credit hours, the student is awarded a (Dual Major) in English Language and Literature.
Career Opportunities:
- Employment in government and private sectors in line with their primary major.
- Writing, reviewing, and editing English content related to their field of specialization.
- Translating specialized and complex materials into clear, field specific guides based on their primary major.
- Supporting communication, training or documentation tasks across various fields, according to their academic specialization.
Graduates are qualified to work in public, private, and non profit sectors, depending on their primary major
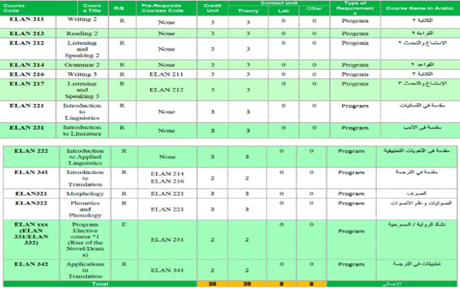
Study Plan:
Course Plan Description:
| No. | Courses | Course Overview | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Writing 2 | This course aims to develop students academic writing skills through the study of various types of essays. Students engage in the full writing process , including prewriting, drafting, revising, and editing, to produce coherent well structured and unified essays. The course also focuses on writing mechanics, vocabulary selection, and effective paragraph transitions | |
| 2 | Reading 2 | The course aims to develop core reading and analytical skills through the study of diverse topics. Students are introduced to vocabulary and expressions related to the texts, along with reading comprehension passages. The course primarily focuses on strengthening key reading strategies , including identifying main ideas and supporting details, mastering summarizing and paraphrasing skills and enhancing critical ability to distinguish between facts and opinions | |
| 3 | Listening and Speaking 2 | The course aims to enhance students proficiency in listening comprehension and oral communication skills. Throughout the course, students develop a deeper understanding of spoken English, with a focus on both formal and informal language varieties | |
| 4 | Grammar 2 | The course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of core grammatical concepts to develop language skills and enhance comprehension. It places particular emphasis on intermediate level grammatical structures and offers ample opportunities for practical application across various language skills. By the end of the course, students are expected to demonstrate accurate and effective use of the specified grammatical concepts | |
| 5 | Writing 3 | The course aims to train students to write organized and meaningful essays on topics of interest. Students engage in the full writing process, including prewriting, drafting, revising, and editing, to produce coherent and effective essays in various genres such as descriptive, narrative, expository, and argumentative writing. The course also emphasizes the appropriate use of linguistic features and writing conventions to generate, summarize, quote, outline, and paraphrase ideas, with attention to both form and content | |
| 6 | Listening and Speaking 3 | This course builds on the foundations covered in Listening and Speaking II. It aims to enhance students’ expressive skills in various contexts, such as classroom presentations and public speaking. The course focuses on developing the ability to understand main ideas and key details during discussions, express agreement or disagreement effectively, demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships, maintain an appropriate speaking pace, and conclude discussions or presentations in a polished manner. In addition, students acquire essential grammatical structures to support accurate proficiency in both spoken and written English | |
| 7 | Introduction to linguistics | The course provides students with a concise overview of the branches of modern linguistics, including phonetics and phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. It primarily aims to prepare students for advanced linguistics courses by approaching language as a structured system that integrates form and meaning, while also highlighting the biological, psychological, cultural, and social aspects of language use. | |
| 8 | Introduction to literature | The course serves as an introduction to literature in its various genres, including poetry, drama, and the novel. Students are introduced to the literary elements specific to each genre and are guided to identify and analyze these elements in literary works. The course also focuses on the development of literature through the study of major writers in the literary tradition, and familiarizes students with literary terms and the techniques of poetry, drama, and the novel. | |
| 9 | Introduction to applied linguistics | The course aims to introduce students to the various branches of applied linguistics, with a focus on its traditional or narrower scope. It primarily covers the major theories, assumptions, methods, processes, and concepts related to different aspects of language learning and teaching, including assessment and error analysis. | |
| 10 | Introduction to translation | The course aims to introduce students to various translation methods and techniques, with a focus on developing their practical skills in translating different types of texts. It seeks to ensure a professional and academic level consistent with the expectations of a university graduate, and to prepare students to address linguistic and cultural challenges across diverse translation contexts. | |
| 11 | Morphology | The course aims to provide students with essential terminology, concepts, and linguistic theories related to morphology. It introduces the development of the English language with particular emphasis on word structure, enabling students to expand their vocabulary and understand word formation. The course also aims to help students achieve proficiency in English and its morphological and linguistic structure. | |
| 12 | Phonetics and Phonology | The course consists of two parts. In the first part, students learn how to produce and distinguish English speech sounds, including consonants, vowels, and diphthongs, using phonetic features. In the second part, students are introduced to phonological processes, syllables, and word segmentation, with an emphasis on mastering phonetic transcription. The course also introduces stress and intonation in English, and trains students to identify intonation patterns by applying rhythmic structure to various data sets. | |
| 13 | Rise of the Novel | In this course, students explore the development of the novel as a literary genre and its historical significance. They examine its origins and evolution from early forms to its establishment as a prominent mode of narrative, while considering the social, cultural, and political contexts that contributed to its rise. The course covers major literary movements, styles, and innovations within the genre, and engages students in critical discussions and written analyses of selected novels, with a focus on themes, narrative techniques, and the novel’s impact on society. | |
| 14 | Drama | In this course, students study dramatic literature and theatrical performance from ancient Greek tragedies to contemporary works. They analyze core elements of drama such as plot, character, dialogue, and stagecraft to understand the power of theatrical storytelling. The course also examines the cultural, social, and political contexts of plays and their impact on society. Students engage in critical discussions, practical exercises, and live performances to gain a comprehensive appreciation of theatre as both a literary and performing art. | |
| 15 | Applications in Translation | In this course, students explore linguistic and cultural differences between languages beyond literal translation. The course also introduces various language styles and trains students to handle and manage them effectively as translators to ensure accurate and fluent transfer of meaning, while taking into account the cultural and linguistic context of both the source and target texts. | |